模型-视图-掌握器(MVC)是[Xerox PARC](baike.baidu.com/item/Xerox PARC/10693263?fromModule=lemma_inlink)在二十世纪八十年代为编程措辞Smalltalk-80发明的一种软件设计模式,已被广泛利用。后来被推举为Oracle旗下Sun公司[Java EE](baike.baidu.com/item/Java EE/2180381?fromModule=lemma_inlink)平台的设计模式,并且受到越来越多的利用ColdFusion和PHP的开拓者的欢迎。模型-视图-掌握器模式是一个有用的工具箱,它有很多好处,但也有一些缺陷。
2. MVC设计思想MVC(Model View Controller)是软件工程中的一种软件架构模式,它把软件系统分为模型、视图和掌握器三个基本部分。用一种业务逻辑、数据、界面显示分离的方法组织代码,将业务逻辑聚拢到一个部件里面,在改进和个性化定制界面及用户交互的同时,不须要重新编写业务逻辑。

MVC 紧张的核心便是:分层:希望专人干专事,各司其职,职能分工要明确,这样可以让代码耦合度降落,扩展力增强,组件的可复用性增强。
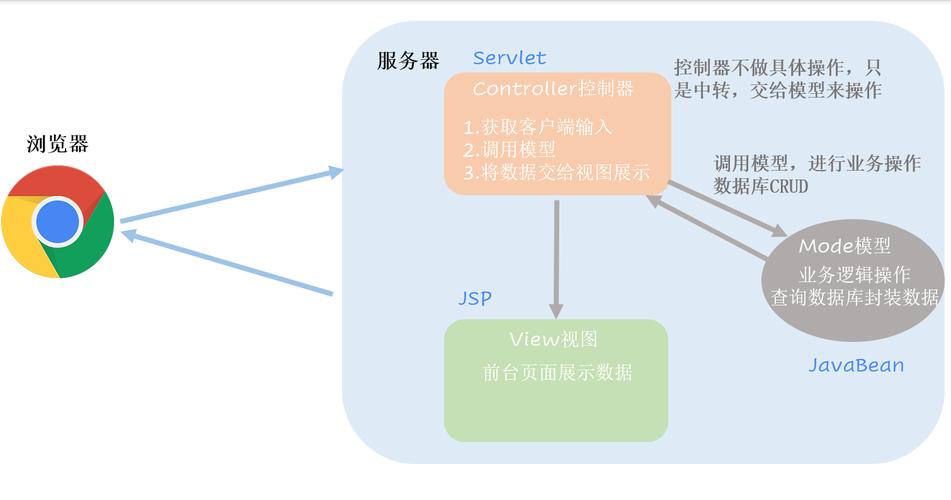
MVC 从字面意思我们就可以看到:是分为了三层的,M(Mode 模型),V(View 视图),C(Controller 掌握器)
M即model模型:是指模型表示业务规则。在MVC的三个部件中,模型拥有最多的处理任务。被模型返回的数据是中立的,模型与数据格式无关,这样一个模型能为多个视图供应数据,由于运用于模型的代码只需写一次就可以被多个视图重用,以是减少了代码的重复性。
V即View视图:是指用户看到并与之交互的界面。比如由html元素组成的网页界面,或者软件的客户端界面。MVC的好处之一在于它能为运用程序处理很多不同的视图。在视图中实在没有真正的处理发生,它只是作为一种输出数据并许可用户操作的办法。
C即controller掌握器:是指掌握器接管用户的输入并调用模型和视图去完成用户的需求,掌握器本身不输出任何东西和做任何处理。它只是吸收要求并决定调用哪个模型构件去处理要求,然后再确定用哪个视图来显示返回的数据。
M(Model :数据/业务) V (View :视图/展示) C (Controller : 掌握层)
C(是核心,是掌握器,是司令官)
M(处理业务/处理数据的一个秘书)
V(卖力页面展示的一个秘书)
MVC(一个司令官,调度两个秘书,去做这件事),仅仅只干事务上的调度,而不做其他的操作
优点:
耦合性低,方便掩护,可以利于分工协作重用性高缺陷:
使得项目架构变得繁芜,对开拓职员哀求高3. 三层架构三层架构(3-tier architecture) 常日意义上的三层架构便是将全体业务运用划分为:界面层[表示层](User Interface layer)、业务逻辑层(Business Logic Layer)、数据访问层(Data access layer)。
区分层次的目的即为了“高内聚低耦合” 的思想。在软件体系架构设计中,分层式构造是最常见,也是最主要的一种构造。
三层架构每层之间的逻辑关系:
三层架构的优点
开拓职员可以只关注全体构造中的个中某一层;可掩护性高,可扩展性高可以降落层与层之间的依赖;有利于标准化;利于各层逻辑的复用三层架构的缺陷:
降落了系统的性能。如果不采取分层式构造,很多业务可以直接拜访数据库,以此获取相应的数据,如今却必须通过中间层来完成有时会导致级联的修正,这种修正尤其表示在自上而下的方向。如果在表示层中须要增加一个功能,为担保其设计符合分层式构造,可能须要在相应的业务逻辑层和数据访问层中都增加相应的代码增加了开拓本钱4. MVC 与 三层架构的关系:MVC的也可以被说成是 MVC三层架构,说白了,它们实在都是一个东西,只是在一些细节上有轻微的不同,大致设计思想都是一样的:“高内聚,低耦合”。
实在,无论是MVC还是三层架构,都是一种规范,都是奔着"高内聚,低耦合"的思想来设计的。三层中的UI和Servlet来分别对应MVC中的View和Controller,业务逻辑层是来组合数据访问层的原子性功能的。
5. 案例举例:用户账户转账如下我们,实现一个用户账户转账操作的一个案例:
准备事情:创建表,创建数据
mysql复制代码CREATE DATABASE mvc;USE mvc;SHOW TABLES;CREATE TABLE t_act ( id BIGINT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT, actno VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL, balance DECIMAL(10,2) );INSERT INTO t_act(actno,balance)VALUES('act001',50000.00),('act002',0.00);SELECT FROM t_act;5.1 M(Model :数据/业务处理层)
javaBean :Account 封装数据
账户实体类,封装账户信息的
一样平常是一张表一个。pojo 工具有的人也会把这种专门封装数据的工具,称为:"bean工具" (javabean工具,咖啡豆)有的人也会把这种专门封装数据的工具,称为领域模型工具,domain工具不同的程序员不同的习气java复制代码package com.RainbowSea.bank.mvc;import java.io.Serializable;import java.util.Objects;/ 账户实体类,封装账户信息的 一样平常是一张表一个。 pojo 工具 有的人也会把这种专门封装数据的工具,称为:"bean工具" (javabean工具,咖啡豆) 有的人也会把这种专门封装数据的工具,称为领域模型工具,domain工具 不同的程序员不同的习气。 /public class Account implements Serializable { // 这种普通的大略的工具被成为pojo工具 // 把稳我们这里定义的数据类型,利用引用数据类型 // 由于我们数据库中可能存在 null 值,而基本数据类型是不可以存储 null值的 private Long id = null; // id private String actno; // 账号 private Double balance; // 余额 // 反序列化 private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; public Account() { } public Account(Long id, String actno, Double balance) { this.id = id; this.actno = actno; this.balance = balance; } public Long getId() { return id; } public void setId(Long id) { this.id = id; } public String getActno() { return actno; } public void setActno(String actno) { this.actno = actno; } public Double getBalance() { return balance; } public void setBalance(Double balance) { this.balance = balance; } @Override public boolean equals(Object o) { if (this == o) return true; if (!(o instanceof Account)) return false; Account account = (Account) o; return Objects.equals(getId(), account.getId()) && Objects.equals(getActno(), account.getActno()) && Objects.equals(getBalance(), account.getBalance()); } @Override public int hashCode() { return Objects.hash(getId(), getActno(), getBalance()); } @Override public String toString() { return "Account{" + "id=" + id + ", actno='" + actno + '\'' + ", balance=" + balance + '}'; }}
DB连接数据库的工具:
properties复制代码driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driverurl=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mvcuser=rootpassword=MySQL
java复制代码package com.RainbowSea.bank.utils;import java.sql.Connection;import java.sql.DriverManager;import java.sql.PreparedStatement;import java.sql.ResultSet;import java.sql.SQLException;import java.util.ResourceBundle;public class DBUtil { // resourceBundle 只能读取到 properties 后缀的文件,把稳不要加文件后缀名 private static ResourceBundle resourceBundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("resources/jdbc"); private static String driver = resourceBundle.getString("driver"); private static String url = resourceBundle.getString("url"); private static String user = resourceBundle.getString("user"); private static String password = resourceBundle.getString("password"); // DBUtil 类加载注册驱动 static { try { Class.forName(driver); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } // 将布局器私有化,不让创建工具,由于工具类中的方法都是静态的,不须要创建工具 // 为了防止创建工具,故将布局方法私有化 private DBUtil() { } / 这里没有利用数据库连接池,直接创建连接工具 / public static Connection getConnection() { Connection connection = null; try { connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password); } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } return connection; } / 资源的关闭 末了利用的最先关闭,逐个关闭,防止存在没有关闭的 / public static void close(Connection connection , PreparedStatement preparedStatement, ResultSet resultSet) { if (resultSet != null) { try { resultSet.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } if (preparedStatement!=null) { try { preparedStatement.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } if (connection != null) { try { connection.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } }}
对应Account数据表的DAO操尴尬刁难象类
AccountDao 是卖力Account 数据的增上改查
什么是DAO ?
Data Access Object (数据访问工具)DAO实际上是一种设计模式,属于 JavaEE的设计模式之一,不是 23种设计模式DAO只卖力数据库表的CRUD ,没有任何业务逻辑在里面没有任何业务逻辑,只卖力表中数据增上改查的工具,有一个特俗的称谓:DAO工具为什么叫做 AccountDao 呢?
这是由于DAO是专门处理t_act 这张表的如果处理t_act 表的话,可以叫做:UserDao如果处理t-student表的话,可以叫做 StudentDao紧张定义如下:增编削查方法()
java复制代码int insert() ;int deleteByActno();int update() ;Account selectByActno();List<Account> selectAll();
java复制代码package com.RainbowSea.bank.mvc;import com.RainbowSea.bank.utils.DBUtil;import java.sql.Connection;import java.sql.PreparedStatement;import java.sql.ResultSet;import java.sql.SQLException;import java.util.Collection;import java.util.List;/ AccountDao 是卖力Account 数据的增上改查 <p> 1. 什么是DAO ? Data Access Object (数据访问工具) 2. DAO实际上是一种设计模式,属于 JavaEE的设计模式之一,不是 23种设计模式 3.DAO只卖力数据库表的CRUD ,没有任何业务逻辑在里面 4.没有任何业务逻辑,只卖力表中数据增上改查的工具,有一个特俗的称谓:DAO工具 5. 为什么叫做 AccountDao 呢? 这是由于DAO是专门处理t_act 这张表的 如果处理t_act 表的话,可以叫做:UserDao 如果处理t-student表的话,可以叫做 StudentDao <p> int insert() ; int deleteByActno(); int update() ; Account selectByActno(); List<Account> selectAll(); /public class AccountDao { / 插入数据 @param account @return / public int insert(Account account) { Connection connection = DBUtil.getConnection(); PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null; int count = 0; try { String sql = "insert into t_act(actno,balance) values(?,?)"; preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); preparedStatement.setString(1, account.getActno()); preparedStatement.setDouble(2, account.getBalance()); count = preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } finally { DBUtil.close(connection, preparedStatement, null); } return count; } / 通过Id删除数据 @param id @return / public int deleteById(String id) { Connection connection = DBUtil.getConnection(); int count = 0; PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null; try { String sql = "delete from t_act where id = ?"; preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); preparedStatement.setString(1, id); count = preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } finally { DBUtil.close(connection, preparedStatement, null); } return count; } / 更新数据 @param account @return / public int update(Account account) { Connection connection = DBUtil.getConnection(); PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null; int count = 0; try { String sql = "update t_act set balance = ?, actno = ? where id = ?"; preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); //把稳设置的 set类型要保持同等。 preparedStatement.setDouble(1, account.getBalance()); preparedStatement.setString(2, account.getActno()); preparedStatement.setLong(3, account.getId()); count = preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } finally { DBUtil.close(connection, preparedStatement, null); } return count; } / 通过 actno 查找账户信息 @param actno @return / public Account selectByActno(String actno) { Connection connection = DBUtil.getConnection(); PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null; ResultSet resultSet = null; Account account = new Account(); try { String sql = "select id,actno,balance from t_act where actno = ?"; preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); //把稳设置的 set类型要保持同等。 preparedStatement.setString(1, actno); resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery(); if (resultSet.next()) { Long id = resultSet.getLong("id"); Double balance = resultSet.getDouble("balance"); // 将结果集封装到java 工具中 account.setActno(actno); account.setId(id); account.setBalance(balance); } } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } finally { DBUtil.close(connection, preparedStatement, resultSet); } return account; } / 查询所有的账户信息 @return / public List<Account> selectAll() { Connection connection = DBUtil.getConnection(); PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null; ResultSet resultSet = null; List<Account> list = null; try { String sql = "select id,actno,balance from t_act"; preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery(); while (resultSet.next()) { String actno = resultSet.getString("actno"); Long id = resultSet.getLong("id"); Double balance = resultSet.getDouble("balance"); // 将结果集封装到java 工具中 Account account = new Account(id,actno,balance); // 添加到List凑集当中 list.add(account); } } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } finally { DBUtil.close(connection, preparedStatement, resultSet); } return list; }}
对指定的数据表的数据进行service 业务逻辑处理操作:
service 翻译为:业务。
AccountService 专门处理Account业务的一个类在该类中该当编写纯业务代码。(只专注域业务处理,不写别的,反面其他代码稠浊在一块)只希望专注业务,能够将业务完美实现,少量bug.业务类一样平常起名:XXXService,XXXBiz...java复制代码package com.RainbowSea.bank.mvc;/ service 翻译为:业务。 AccountService 专门处理Account业务的一个类 在该类中该当编写纯业务代码。(只专注域业务处理,不写别的,反面其他代码稠浊在一块) 只希望专注业务,能够将业务完美实现,少量bug. <p> 业务类一样平常起名:XXXService,XXXBiz... /public class AccountService { // 这里的方法起名,一定要表示出,你要处理的是什么业务: // 我们要供应一个能够实现转账的业务的方法(一个业务对应一个方法) // 比如:UserService StudentService OrderService // 处理Account 转账业务的增编削查的Dao private AccountDao accountDao = new AccountDao(); / 完成转账的业务逻辑 @param fromActno 转出账号 @param toActno 转入账号 @param money 转账金额 / public void transfer(String fromActno, String toActno, double money) throws MoneyNotEnoughException, AppException { // 查询余额是否充足 Account fromAct = accountDao.selectByActno(fromActno); if (fromAct.getBalance() < money) { throw new MoneyNotEnoughException("对不起,余额不敷"); } // 程序到这里解释余额充足 Account toAct = accountDao.selectByActno(toActno); // 修正金额,先从内存上修正,再从硬盘上修正 fromAct.setBalance(fromAct.getBalance() - money); toAct.setBalance(toAct.getBalance() + money); // 从硬盘数据库上修正 int count = accountDao.update(fromAct); count += accountDao.update(toAct); if(count != 2) { throw new AppException("账户转账非常,请联系管理员"); } }}
非常处理类:
java复制代码package com.RainbowSea.bank.mvc;/ 余额不敷非常 /public class AppException extends Exception{ public AppException() { } public AppException(String msg) { super(msg); }}
java复制代码package com.RainbowSea.bank.mvc;/ 余额不敷非常 /public class MoneyNotEnoughException extends Exception{ public MoneyNotEnoughException() { } public MoneyNotEnoughException(String msg) { super(msg); }}5.2 C (Controller : 掌握层)
仅仅卖力调度 M业务处理层,V视图显示层,而不做其他操作。
java复制代码package com.RainbowSea.bank.mvc;import jakarta.servlet.ServletException;import jakarta.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServlet;import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;import java.io.IOException;/ 账户小程序 AccountServlet 是一个司令官,他卖力调度其他组件来完成任务。 /@WebServlet("/transfer")public class AccountServlet extends HttpServlet { // AccountServlet 作为一个 Controller 司令官 @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { // 获取数据 String fromActno = request.getParameter("fromActno"); String toActno = request.getParameter("toActno"); double money = Double.parseDouble(request.getParameter("money")); // 调用业务方法处理业务(调度Model处理业务,个中是对应数据表的 CRUD操作) AccountService accountService = new AccountService(); try { accountService.transfer(fromActno,toActno,money); // 实行到这里解释,成功了, // 展示处理结束(调度 View 做页面展示) response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath()+"/success.jsp"); } catch (MoneyNotEnoughException e) { // 实行到种类,解释失落败了,(余额不敷 // 展示处理结束(调度 View 做页面展示) response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath()+"/error.jsp"); } catch (AppException e) { // 实行到种类,解释失落败了,转账非常 // 展示处理结束(调度 View 做页面展示) response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath()+"/error.jsp"); } // 页面的展示 (调度View做页面展示) }}5.3 V (View :视图/展示)
index.jsp 转账页面:
jsp复制代码<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %><html><head> <title>银行账号转账</title></head><body><form action="<%=request.getContextPath()%>/transfer" method="post"> 转出账户: <input type="text" name="fromActno" /> <br> 转入账户: <input type="text" name="toActno" /> <br> 转账金额: <input type="text" name="money" /><br> <input type="submit" value="转账" /></form></body></html>
success转账成功的页面显示:
jsp复制代码<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %><html><head> <title>转账成功</title></head><body><h3>转账成功</h3></body></html>
error 转账失落败的页面显示:
jsp复制代码<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %><html><head> <title>转账失落败</title></head><body><h3>转账失落败</h3></body></html>
虽然上述:代码成功实现的了用户转账的操作,但是并没有进行事务的处理。
如下是利用 TreadLocal 进行事务的处理: blog.csdn.net/weixin_6163…
6. 总结:MVC 从字面意思我们就可以看到:是分为了三层的,M(Mode 模型),V(View 视图),C(Controller 掌握器)M(Model :数据/业务) V (View :视图/展示) C (Controller : 掌握层)C(是核心,是掌握器,是司令官)M(处理业务/处理数据的一个秘书)V(卖力页面展示的一个秘书)MVC(一个司令官,调度两个秘书,去做这件事),仅仅只干事务上的调度,而不做其他的操作三层架构(3-tier architecture) 常日意义上的三层架构便是将全体业务运用划分为:界面层[表示层](User Interface layer)、业务逻辑层(Business Logic Layer)、数据访问层(Data access layer)。无论是MVC还是三层架构,都是一种规范,都是奔着"高内聚,低耦合"的思想作者:RainbowSea链接:https://juejin.cn/post/7234060427412668471