一、问题引入
在日常写项目的时候,肯定少不了要打印日志。例如,要向数据库中insert一个用户,我想在插入前输出一下干系信息,怎么实现呢?最基本的做法是:在insert方法中写日志输出语句。这样写完备能实现功能,但是会不会显得很冗余?耦合度是不是很高?编程的准则是“高内聚,低耦合”,低耦合的意思便是类与类之间的依赖关系只管即便少、关联程度只管即便小。

而如果在上述情景中利用面向切面编程(AOP),就可以不在insert方法中写日志输出语句却能实现日志输出功能。当然,AOP不止如此。
二、观点引入
1.AOP
在软件业,AOP为Aspect Oriented Programming的缩写,意为:面向切面编程,通过预编译方 式和运行期动态代理实现程序功能的统一掩护的一种技能。AOP是OOP的延续,是软件开拓中的一个 热点,也是Spring框架中的一个主要内容,是函数式编程的一种衍生范型。利用AOP可以对业务逻辑 的各个部分进行隔离,从而使得业务逻辑各部分之间的耦合度降落,提高程序的可重用性,同时提高 了开拓的效率。
2.几个基本观点
- 切入点:所有要操作的方法定义,哀求业务层方法风格统一- 分离点:将不可分割的组件单独提取出去定义为单独的操作功能- 横切关注点:将所有与开拓无关的程序组成类单独提取后组织运行- 织入:将所有切入点、关注点的代码组成在一张完全的程序构造中
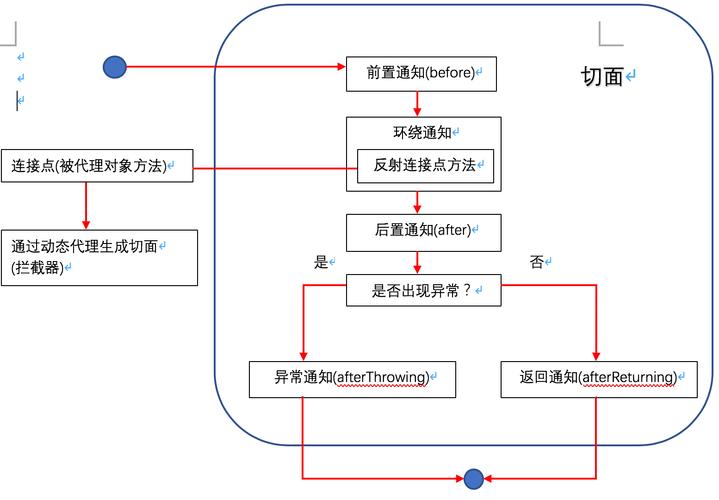
3.关照(Advice)
AOP是通过关照来实现功能的,有如下五种:
前置关照(BeforeAdvice)后置关照(AfterAdvice)后置返回关照(AfterReturningAdvice)后置非常关照(AfterThrowingAdvice)环抱关照(AroundAdvice)三、Pointcut与Execution表达式
pointcut利用execution表达式表示要被切入的方法(即定义切入点)。
execution表达式,功能类似于正则表达式,都是用来匹配筛选,只不过正则表达式用来筛选字符串,而execution表达式用来筛选要被切入的方法。
execution表达式的格式为:
execution(<表明>? <润色符>? <返回值类型> <方法名模式>(<参数模式>) <非常>?)) <and args()>?)
例:execution(@Deprecated public Void aop.MyAspect.hello(int,String) throws Exception))')
package aop;public class AspectDemo { @Deprecated public void hello(int i,String s) throws Exception{ }}
实在不难创造,这个表达式和我们声明的方法的各个部分逐一对应
表明:(可省略)例如上面代码中的@Deprecated ,便是筛选带有该表明的方法润色符(可省略)publicprotectedprivate当然一样平常用通配符 返回值类型写各种返回值,一样平常用通配符 方法名模式包名部分:在上例中,AspectDemo是位于aop包中的,以是可以通过包名.包名.类名的格式来定位到某个类,例如aop.AspectDemo 中aop. 便是包名部分;当然也可以用通配符:匹配任何数量字符,例如service..UserService 表示的是service的直接子包..:匹配任何数量字符的重复,如在类型模式中匹配任何数量子包,例如service..代表着匹配service及其包含的所有包;而在方法参数模式中匹配任何数量参数。+: 匹配指定类型的子类型;仅能作为后缀放在类型模式后边,例如java.lang.Number+ 表示的是lang包下Numer的子类类名部分:在上例中aop.AspectDemo中aop.是包名部分,AspectDemo便是类名部分,可以用通配符来表示,用的比较多参数模式写法1:直接按照方法的参数列表写详细类型,上例的方法中参数列表(int i,String s),就可以直接在表达式中写(int,String)写法2:利用通配符:“()”表示方法没有任何参数;“(..)”表示匹配接管任意个参数的方法“(..,java.lang.String)”表示匹配接管java.lang.String类型的参数结束,且其前边可以接管有任意个参数的方法“(java.lang.String,..)” 表示匹配接管java.lang.String类型的参数开始,且其后边可以接管任意个参数的方法“(,java.lang.String)” 表示匹配接管java.lang.String类型的参数结束,且其前边接管有一个任意类型参数的方法;非常模式(可省略)throws Exception1,Exception2.。。。传入参数(可省略) and args(arg-name),一样平常用于AfterAdvice和Around关照四、前期准备
创建项目,导入干系jar包,参考Spring——IOC,此外还需导入aop和aspectj的jar包创建applicationContext.xml文件<?xml version=\"大众1.0\"大众 encoding=\"大众UTF-8\公众?><beans xmlns=\"大众http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans\"大众 xmlns:xsi=\公众http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance\"大众 xmlns:context=\"大众http://www.springframework.org/schema/context\"大众 xmlns:aop=\"大众http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop\公众 xsi:schemaLocation=\"大众 http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd\"大众> <aop:aspectj-autoproxy/></beans>
把稳:新增了
xmlns:aop=\"大众http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop\"大众
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-aop.xsd
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/> 不加这个可能会报错,可坑了
创建UserService这个类,内部有insert方法用来注册用户public class UserService { public void insert(){ System.out.println(\"大众UserService正在注册用户……\"大众); }}创建MyAspect类
public class MyAspect {}
五、基于XML配置的AOP
1.BeforeAdvice
(1)在MyAspect类中创建方法beforeAdvice
public void beforeAdvice(){ System.out.println(\公众【AOP】Before Advice正在实行……\"大众); }
(2)在applicationContext.xml中配置
关于pointcut和execution表达式见下文
<!--首先要引入myAspect这个bean,备用--> <bean id=\"大众myAspect\"大众 class=\公众aop.MyAspect\公众/> <bean id=\"大众userService\公众 class=\"大众aop.UserService\"大众/> <aop:config> <!--配置切面,一个aop:aspect标签对应一个Aspect类--> <aop:aspect id=\"大众beforeAdvice\"大众 ref=\公众myAspect\"大众> <!--配置关照 method对应MyAspect类中定义的方法,pointcut是切入点表达式用于筛选须要被 切入的方法--> <aop:before method=\公众beforeAdvice\"大众 pointcut=\公众execution( aop...(..)))\"大众/> </aop:aspect> </aop:config>
(3)编写测试类
public class UserServiceTest { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext context= new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(\公众applicationContext.xml\"大众); UserService userService = context.getBean(\公众userService\公众, UserService.class); userService.insert(); }}
(4)输出结果
【AOP】Before Advice正在实行…… UserService正在注册用户……
可以创造,BeforeAdvice就已经实现了
2.AfterAdvice(相称于非常里面的finally语句)
(1)UserService类同上
(2)在MyAspect中创建方法afterAdvice
public void afterAdvice(){ System.out.println(\"大众【AOP】after Advice…… 不管若何我都会实行\"大众);}
(3)修正applicationContext.xml
<aop:config> <aop:aspect id=\公众beforeAdvice\公众 ref=\"大众myAspect\"大众> <aop:after method=\公众afterAdvice\"大众 pointcut=\公众execution( aop..insert(..)))\"大众 /> </aop:aspect></aop:config>
(4)编写测试类(同上)
(5)输出结果
UserService正在注册用户……【AOP】after Advice…… 不管若何我都会实行
3.AfterReturningAdvice
(1)修正UserService的insert方法,使其有返回值
public class UserService { public int insert(){ System.out.println(\"大众UserService正在注册用户……\公众); return 1; }}
(2)在MyAspect中新增afterReturningAdvice方法
public void afterReturningAdvice(int result) { System.out.println(\公众【AOP】after advice……返回值为\"大众+result); }
(3)在applicationContext.xml中配置
<aop:config> <aop:aspect id=\"大众beforeAdvice\"大众 ref=\公众myAspect\公众> <aop:after-returning method=\"大众afterReturningAdvice\"大众 pointcut=\"大众execution( aop..insert(..)))\"大众 returning=\"大众result\"大众/> </aop:aspect></aop:config>
把稳:这里这个returning=\"大众result\"大众与MyAspect类中对应方法的参数名必须保持同等,本例中都为result
(4)编写测试类(代码同1.)
(5)输出结果
UserService正在注册用户…… 【AOP】after advice……返回值为1
4.AfterThrowingAdvice
(1)修正UserService使其抛非常
public int insert() throws Exception { try { System.out.println(\"大众UserService开始注册用户……\"大众); int i=1/0; }catch (Exception e){ throw new Exception(\"大众insert方法碰着非常……\"大众); } return 1;}
(2)在MyAspect中新增方法 afterThrowingAdvice
//这里传入的这个Exception便是捕获到的非常工具public void afterThrowingAdvice(Exception e){ System.out.println(\公众【AOP】得到非常信息:\公众+e.getMessage());}
(3)修正applicationContext.xml
<aop:config> <aop:aspect id=\"大众beforeAdvice\"大众 ref=\"大众myAspect\公众> <aop:after-throwing method=\"大众afterThrowingAdvice\"大众 pointcut=\公众execution( aop..insert(..)))\公众 throwing=\"大众e\公众/> </aop:aspect></aop:config>
把稳:这里的throwing=\"大众e”便是跑出的非常工具的名字,要与MyAspect中afterThrowingAdvice方法中传入的参数Exception e的名字保持同等。
(4)编写测试类
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { ApplicationContext context= new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(\公众applicationContext.xml\公众); UserService userService = context.getBean(\"大众userService\"大众, UserService.class); userService.insert();}
(5)输出结果
UserService开始注册用户……【AOP】得到非常信息insert方法碰着非常……Exception in thread \"大众main\"大众 java.lang.Exception: insert方法碰着非常…… at aop.UserService.insert(UserService.java:12) at aop.UserService$$FastClassBySpringCGLIB$$7e3b8e5e.invoke(<generated>) ...
5.AroundAdvice
(1)修正UserService中的insert方法
public int insert(int arg) throws Exception { try { int i = 1 / 0; } catch (Exception e) { throw new Exception(\"大众insert方法碰着非常……\公众); } return 1;}
(2)在MyAspect中添加方法AroundAdvice
//这里这个ProceedingJointPoint可以理解为切入点工具,可以通过它获取切入点(被切入的方法)的参数、返回值、抛出的非常,并且可以通过pjp.proceed(args);为该切入点设置参数public int aroundAdvice(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable { Object[] args = pjp.getArgs(); System.out.println(\公众【AOP】before Advice,获取到insert方法传入的参数为:\"大众+args[0]); Object result; try { result=pjp.proceed(args);//这里是我们手动实行切入点,并传入参数 System.out.println(\"大众【AOP】after Returning Advice,返回值为:\公众+result); }catch (Exception e){ //这里捕获的便是切入点运行时抛出的非常 System.out.println(\公众【AOP】after Throwing Advice,缺点信息为:\公众+e.getMessage()); } System.out.println(\公众【AOP】after advice……不管非常不非常我都实行\"大众); //这个就随着这样写吧。。如果不写返回值的话会报 null return value does not match... return 1;}
(3)修正applicationContext.xml文件
<aop:config> <aop:aspect id=\公众beforeAdvice\"大众 ref=\"大众myAspect\"大众> <aop:around method=\公众aroundAdvice\"大众 pointcut=\公众execution( aop..insert(..)))\公众 /> </aop:aspect></aop:config>
(4)编写测试类
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { ApplicationContext context= new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(\"大众applicationContext.xml\"大众); UserService userService = context.getBean(\公众userService\公众, UserService.class); userService.insert(2);}
(5)输出结果
【AOP】before Advice,获取到insert方法传入的参数为:2【AOP】after Throwing Advice,缺点信息为:insert方法碰着非常……【AOP】after advice……不管非常不非常我都实行
六、基于表明配置的AOP
先把项目状态规复到 “四、前期准备”的状态,然后在applicationContext.xml中添加下面的语句开启表明和包扫描。
<context:annotation-config/><context:component-scan base-package=\公众aop\"大众/>
把稳,这个base-package可以配置多个包,以半角(英文)逗号隔开,例如“aop,mvc,dao,service”,当然,为了省事,可以直接配一个顶级包,他会自动遍历扫描所有的子包及子包的子包等等。
然后为MyAspect类和UserService类加上表明
@Component@Aspectpublic class MyAspect {}@Servicepublic class UserService {}
1.BeforeAdvice
(1)在MyAspect类中创建beforeAdvice方法,并写好表明
@Before(value = \公众execution( aop...(..)))\"大众)public void beforeAdvice(){ System.out.println(\公众【AOP】Before Advice正在实行……\"大众);}
不须要配任何bean,是不是很爽
(2)编写测试类
public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext context= new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(\"大众applicationContext.xml\公众); UserService userService = context.getBean(\"大众userService\公众, UserService.class); userService.insert();}
(3)输出结果
【AOP】Before Advice正在实行…… UserService正在注册用户……
2.AfterService(我就不写测试了)
(1)在MyAspect类中创建afterAdvice方法,并写好表明
@After(value = \"大众execution( aop...(..)))\公众)public void afterAdvice(){ System.out.println(\"大众【AOP】after Advice正在实行……\"大众);}
3.AfterReturningAdvice
(1)修正UserService中的insert方法
public int insert(){ System.out.println(\公众UserService正在注册用户……\公众); return 1;}
(2)在MyAspect类中创建afterReturningAdvice方法,并写好表明
@AfterReturning(value = \公众execution( aop...(..))&& args(result))\公众)public void afterReturningAdvice(int result){ System.out.println(\公众【AOP】after Returning Advice正在实行……返回值为:\"大众+result);}
(3)不写测试了
4.AfterThrowingAdvice
(1)修正UserService中的insert方法
public int insert() throws Exception { try { int i=1/0; }catch (Exception e){ throw new Exception(\"大众【UserService】的insert碰着了缺点……\"大众); } return 1;}
(2)在MyAspect类中创建afterThrowingAdvice方法,并写好表明
@AfterThrowing(value = \公众execution( aop...(..)))\公众,throwing = \"大众e\公众)public void afterThrowingAdvice(Exception e){ System.out.println(\"大众【AOP】after Throwing Advice正在实行……缺点信息为:\公众+e.getMessage());}
(3)不测试了。。
5.AroundAdvice
(1)把MyAspect中之前写的方法注释掉,不然会影响不雅观察结果
(2)修正insert方法
public int insert(int arg) throws Exception { try { int i=1/0; }catch (Exception e){ throw new Exception(\"大众【UserService】的insert碰着了缺点……\公众); } return 1;}
(3)在MyAspect类中创建aroundAdvice方法,并写好表明
@Around(value = \"大众execution( aop...(..)))\公众)public int aroundAdvice(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable { Object[] args = pjp.getArgs(); System.out.println(\公众【AOP】before Advice,获取到insert方法传入的参数为:\"大众+args[0]); Object result; try { result=pjp.proceed(args); System.out.println(\"大众【AOP】after Returning Advice,返回值为:\"大众+result); }catch (Exception e){ System.out.println(\公众【AOP】after Throwing Advice,缺点信息为:\"大众+e.getMessage()); } System.out.println(\"大众【AOP】after advice……不管非常不非常我都实行\"大众); return 1;}
关注作者:JAVA高等程序员
专注分享:(高可用、高并发、高性能及分布式、Jvm性能调优、Spring源码,MyBatis,Netty,Redis,Kafka,Mysql,Zookeeper,Tomcat,Docker,Dubbo,Nginx等技能...)
欢迎转发,评论~~~每天Java一下,成为架构师!