现在直播行业大火,有斗鱼、虎牙等这种大型直播平台,也有带货直播、电商直播等等,这些直播都会有弹幕系统,没有弹幕的直播是没有灵魂的。不止是直播类,你在各大视频网站看视频时,不开弹幕吗?!
!
有时弹幕比视频内容更好看。
弹幕系统的利用场景非常广泛,其紧张特点是实时性高、并发量大,尤其是并发量。在直播场景中,每每一个大主播,一场直播下来百万弹幕轻轻松松。由于golang在并发场景中的优胜表现,我们选择利用golang来实现弹幕系统。

弹幕系统肯定绕不开websocket协议,利用弹幕的系统基本都会有H5运用,H5运用上的弹幕系统,大家想到切实其实定是用websocket实现。
各大措辞都有很多现成的websocket类库,例如nodeJS的socket.io,PHP的swoole等等,项目的一开始我们不该用这些现成的库,我们自己实现一个大略的websocket协议,在实现过程中学习websocket协议。
websocket协议在RFC6455中详细描述,有大神翻译的中文版了。
闲话不多说,下面开始动手。
websocket在建立握手时,是基于HTTP做事的,我们先启动一个HTTP做事:
func main() { http.HandleFunc("/echo", func(writer http.ResponseWriter, request http.Request) { serveWs(writer, request) }) err := http.ListenAndServe("localhost:9527", nil) if err != nil { log.Fatal(err) }}复制代码
我们先用一个echo做事来测试websocket协议的实现,端口为9527,函数serveWs的功能很大略,建立socket连接,读取信息并回写,即一个echo做事。
握手连接RFC6455文档第4节详细先容了握手建立的过程。我们照着文档一步步实现。
The method of the request MUST be GET, and the HTTP version MUST be at least 1.1.
HTTP的方法必须是GET方法:
if request.Method != "GET" { return nil, fmt.Errorf("HTTP必须是GET方法")}复制代码
The request MUST contain an Upgrade header field whose value MUST include the "websocket" keyword.
必须要有Upgradeheader,它的值必须是websocket:
if !httpHeaderContainsValue(request.Header, "Upgrade", "websocket") { return nil, fmt.Errorf("必须包含一个Upgrade header字段,它的值必须为websocket")}复制代码
等等一系列的校验,这里就不一一赘述了。
HTTP header验证完后,我们再来处理TCP连接,众所周知,HTTP是在TCP之上的运用层协议,正常情形下,一个HTTP要求结束后,TCP也会断开。websocket连接实在便是一个TCP连接,以是我们不能让这个HTTP中的这个TCP连接断开,我们自己来管理这个TCP连接。怎么获取HTTP中的TCP连接呢?Golang为我们供应了一个Hijack方法。
hijacker, ok := writer.(http.Hijacker)if !ok { return nil, fmt.Errorf("未实现http.Hijacker")}netConn, buf, err := hijacker.Hijack()if err != nil { return nil, err}复制代码
吸收到客户真个握手要求后,我们必须相应前真个要求,才能完玉成部握手的过程。
If the status code received from the server is not 101, the client handles the response per HTTP [RFC2616] procedures. In particular, the client might perform authentication if it receives a 401 status code; the server might redirect the client using a 3xx status code (but clients are not required to follow them), etc. Otherwise, proceed as follows.
我们只是大略实现一个websocket协议,这里直接设置状态码为101:
var response []byteresponse = append(response, "HTTP/1.1 101 Switching Protocols\r\n"...)复制代码
If the response lacks an |Upgrade| header field or the |Upgrade| header field contains a value that is not an ASCII case- insensitive match for the value "websocket", the client MUST Fail the WebSocket Connection.
相应中必须有Upgradeheader信息,且值必须为websocket(不区分大小写):
response = append(response, "Upgrade: websocket\r\n"...)复制代码
If the response lacks a |Connection| header field or the |Connection| header field doesn't contain a token that is an ASCII case-insensitive match for the value "Upgrade", the client MUST Fail the WebSocket Connection.
必须有Connection且值必须为Connection:
response = append(response, "Connection: Upgrade\r\n"...)复制代码
If the response lacks a |Sec-WebSocket-Accept| header field or the |Sec-WebSocket-Accept| contains a value other than the base64-encoded SHA-1 of the concatenation of the |Sec-WebSocket- Key| (as a string, not base64-decoded) with the string "258EAFA5- E914-47DA-95CA-C5AB0DC85B11" but ignoring any leading and trailing whitespace, the client MUST Fail the WebSocket Connection.
必须有Sec-WebSocket-Acceptheader,值要根据Sec-WebSocket-Key的值和"258EAFA5-E914-47DA-95CA-C5AB0DC85B11"串联起来,忽略所有前后空格进行base64 SHA-1编码得到:
var acceptKeyGUID = []byte("258EAFA5-E914-47DA-95CA-C5AB0DC85B11")generateAcceptKey(request.Header.Get("Sec-WebSocket-Key"))func generateAcceptKey(key string) string { h := sha1.New() h.Write([]byte(key)) h.Write(acceptKeyGUID) return base64.StdEncoding.EncodeToString(h.Sum(nil))}response = append(response, "Sec-WebSocket-Accept: "...)response = append(response, generateAcceptKey(request.Header.Get("Sec-WebSocket-Key"))...)response = append(response, "\r\n\r\n"...)复制代码
其他的非必选信息我们就不添加了。header布局好后,相应给客户端:
if _, err = netConn.Write(response); err != nil { netConn.Close()}复制代码
由于现在这个TCP连接是我们自己管理,以是当握手过程中涌现失落败时,须要我们自己关闭这个连接。
现在,我们已经完成了全体握手的过程。测试一下:
握手成功,接下来我们开始详细的收发处理。
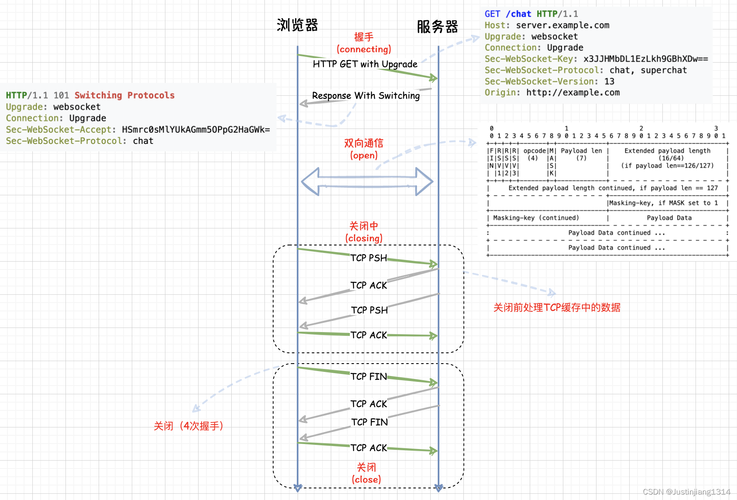
读在WebSocket协议中,数据是通过一系列数据帧来进行传输的,RFC6455中第5节详情先容了数据帧。
根本数据帧格式:
0 1 2 3 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 +-+-+-+-+-------+-+-------------+-------------------------------+ |F|R|R|R| opcode|M| Payload len | Extended payload length | |I|S|S|S| (4) |A| (7) | (16/64) | |N|V|V|V| |S| | (if payload len==126/127) | | |1|2|3| |K| | | +-+-+-+-+-------+-+-------------+ - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - + | Extended payload length continued, if payload len == 127 | + - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - +-------------------------------+ | |Masking-key, if MASK set to 1 | +-------------------------------+-------------------------------+ | Masking-key (continued) | Payload Data | +-------------------------------- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - + : Payload Data continued ... : + - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - + | Payload Data continued ... | +---------------------------------------------------------------+复制代码
摘录一些主要的信息:
FIN: 1 bit
Indicates that this is the final fragment in a message. The first fragment MAY also be the final fragment. 复制代码
RSV1, RSV2, RSV3: 1 bit each
MUST be 0 unless an extension is negotiated that defines meanings for non-zero values. If a nonzero value is received and none of the negotiated extensions defines the meaning of such a nonzero value, the receiving endpoint MUST _Fail the WebSocket Connection_. 复制代码
Opcode: 4 bits
Defines the interpretation of the "Payload data". If an unknown opcode is received, the receiving endpoint MUST _Fail the WebSocket Connection_. The following values are defined. %x0 denotes a continuation frame %x1 denotes a text frame %x2 denotes a binary frame %x3-7 are reserved for further non-control frames %x8 denotes a connection close %x9 denotes a ping %xA denotes a pong %xB-F are reserved for further control frames 复制代码
Mask: 1 bit
Defines whether the "Payload data" is masked. If set to 1, a masking key is present in masking-key, and this is used to unmask the "Payload data" as per Section 5.3. All frames sent from client to server have this bit set to 1. 复制代码
Payload length: 7 bits, 7+16 bits, or 7+64 bits
The length of the "Payload data", in bytes: if 0-125, that is the payload length. If 126, the following 2 bytes interpreted as a 16-bit unsigned integer are the payload length. If 127, the following 8 bytes interpreted as a 64-bit unsigned integer (the most significant bit MUST be 0) are the payload length. Multibyte length quantities are expressed in network byte order. Note that in all cases, the minimal number of bytes MUST be used to encode the length, for example, the length of a 124-byte-long string can't be encoded as the sequence 126, 0, 124. The payload length is the length of the "Extension data" + the length of the "Application data". The length of the "Extension data" may be zero, in which case the payload length is the length of the "Application data". 复制代码
Masking-key: 0 or 4 bytes
All frames sent from the client to the server are masked by a 32-bit value that is contained within the frame. This field is present if the mask bit is set to 1 and is absent if the mask bit is set to 0. See Section 5.3 for further information on client- to-server masking. 复制代码
Payload data: (x+y) bytes
The "Payload data" is defined as "Extension data" concatenated with "Application data". 复制代码
在开始解析数据帧之前,我们来定义一些数据构造和方法:
type Conn struct { conn net.Conn br bufio.Reader writeBuf []byte // 写缓存 readLength int64 //数据长度 maskKey [4]byte // mask key}// 数据帧位// RFC6455 5.2节const ( finalBit = 1 << 7 rsv1Bit = 1 << 6 rsv2Bit = 1 << 5 rsv3Bit = 1 << 4 opCode = 0xf maskBit = 1 << 7 pladloadLen = 0x7f)// 类型// RFC6455 5.2节或11.8节const ( ContinuationMessage = 0 TextMessage = 1 BinaryMessage = 2 CloseMessage = 8 PingMessage = 9 PongMessage = 10)func (c Conn)read(n int) ([]byte, error) { // 读取n个字节数据 p, err := c.br.Peek(n) // 丢弃掉n个字节数据 c.br.Discard(len(p)) return p, err}func newConn(conn net.Conn, br bufio.Reader) Conn { c := &Conn{ conn:conn, br:br, writeBuf:make([]byte, 128), // 写去世,只接管128字节数据 } return c}复制代码读取数据帧头信息
在网络中,数据因此字节为单位进行传输的。在websocket中,主要的头信息都在前2个字节中,读取前2个字节:
p, err := c.read(2)if err != nil { return err}// 解析数据帧 RFC6455 5.2节// 逼迫按0判断,不考虑是否有扩展信息if rsv := p[0] & (rsv1Bit | rsv2Bit | rsv3Bit); rsv != 0 { return fmt.Errorf("RSV必须为0")}// 表示这是的末了一个片段。第一个片段也有可能是末了一个片段。// 暂时不考虑FIN位信息// final := p[0]&finalBit != 0frameType := int(p[0]&opCode)// 判断FIN和opcode为是否匹配// RFC6455 5.4节// todoswitch frameType {case ContinuationMessage:case TextMessage, BinaryMessage:case CloseMessage, PingMessage, PongMessage:default: return fmt.Errorf("未知的opcode")}复制代码
All frames sent from client to server have this bit set to 1.
客户真个数据帧中mask位必须为1:
mask := p[1]&maskBit != 0if !mask { return fmt.Errorf("mask位必须标记为1")}复制代码
再来获取运用数据的长度
Payload length: 7 bits, 7+16 bits, or 7+64 bits
c.readLength = int64(p[1]&pladloadLen)复制代码
如果数据长度小于即是125,实际的值便是运用数据的长度。如果即是126,那么接下来的2个字节阐明为一个16bit的无符号整形,作为运用数据的长度。如果即是127,那么接下来的8个字节阐明为一个64bit的无符号整形,作为运用数据的长度。
// 获取数据长度// https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6455#section-5.2// The length of the "Payload data", in bytes: if 0-125, that is the// payload length. If 126, the following 2 bytes interpreted as a// 16-bit unsigned integer are the payload length. If 127, the// following 8 bytes interpreted as a 64-bit unsigned integer (the// most significant bit MUST be 0) are the payload length. Multibyte// length quantities are expressed in network byte order.c.readLength = int64(p[1]&pladloadLen)switch c.readLength {case 126: p, err := c.read(2) if err != nil { return err } c.readLength = int64(binary.BigEndian.Uint16(p))case 127: p, err := c.read(8) if err != nil { return err } c.readLength = int64(binary.BigEndian.Uint64(p))}复制代码
获取mask-key掩码:
Masking-key: 0 or 4 bytes
p, err := c.read(4)if err != nil { return err}复制代码
我们只发送最大略的数据,其他数据帧信息都不存在,我们就不兼容处理了。
读取运用数据读取运用数据就大略了:
// 读取长度加1,是为了大略处理,直接将EOF也读取出来var p = make([]byte, c.readLength+1)n, err := c.br.Read(p)if err != nil { return nil, err}复制代码
由于读取的数据是掩码之后的数据,以是我们须要解码。掩码和解码的算法5.3节已详细先容过。
Octet i of the transformed data ("transformed-octet-i") is the XOR of octet i of the original data ("original-octet-i") with octet at index i modulo 4 of the masking key ("masking-key-octet-j"):
j = i MOD 4 transformed-octet-i = original-octet-i XOR masking-key-octet-j 复制代码
// 只支持英文和数字func maskBytes(key [4]byte, pos int, b []byte) int { for i := range b { b[i] ^= key[pos%4] pos++ } return pos%4}maskBytes(c.maskKey, 0, p[:n])复制代码
测试一下:
$ go run .gorsv msg WebSocket rocks复制代码
数据读取成功。下面开始写信息。
写运用数据连续大略处理,只支持写125字节的数据。由于超过125字节的数据,Payload len位就要做分外处理了。这样的话,紧张的头信息就在前2个字节中了。
逼迫文本信息,并且RSV都设置0,FIN直接为1:
// 第一个字节(前8位)// 默认为文本信息b0 := byte(TextMessage)// FIN 1b0 |= finalBit复制代码
然后设置MASK位和运用数据长度:
b1 := byte(0)b1 |= byte(len(msg))复制代码
由于这里已经限定只能写不超过125字节的数据了,以是可以直接设置Payload len位。 写入缓存:
c.writeBuf[0] = b0c.writeBuf[1] = b1复制代码
头信息设置完了,可以写运用数据了:
func (c Conn) WriteMessage(msg []byte) error { ... copy(c.writeBuf[2:], msg) _, err := c.conn.Write(c.writeBuf) return err}复制代码
再来测试一下:
至此,我们一个超大略、只能学习用的websocket协议实现了。
websocket的扩展信息和二进制类型的信息我们都没处理,ping、pong等都没处理,而且数据分片、粘包处理等等我们都没处理。以是说,这只是学习用。
项目的代码地址gitee.com/ask/danmaku
作者:W_