在Java中,可以通过创建一个链表节点类,然后遍历数组并逐个创建链表节点来将数组转换成链表操作。如下所示。
第一步、定义链表节点这里我们先来大略的定义一个单链表构造,如下所示。

// 定义链表节点类class ListNode { int val; ListNode next; ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; this.next = null; }}第二步、实现链表转换
// 将数组转换成链表的方法public static ListNode arrayToLinkedList(int[] array) { if (array == null || array.length == 0) { return null; // 如果数组为空,返回null } // 创建链表头节点 ListNode head = new ListNode(array[0]); ListNode current = head; // 遍历数组,创建链表节点并链接 for (int i = 1; i < array.length; i++) { current.next = new ListNode(array[i]); current = current.next; } return head; // 返回链表头节点}
首先先来检讨数组的长度是否为0,如果为0则直接返回null,否则连续实行后续操作。创建链表的头节点,并初始化为数组的第一个元素。接下来便是遍历数组创建节点将其连接到后续的节点上,终极返转头结点工具。
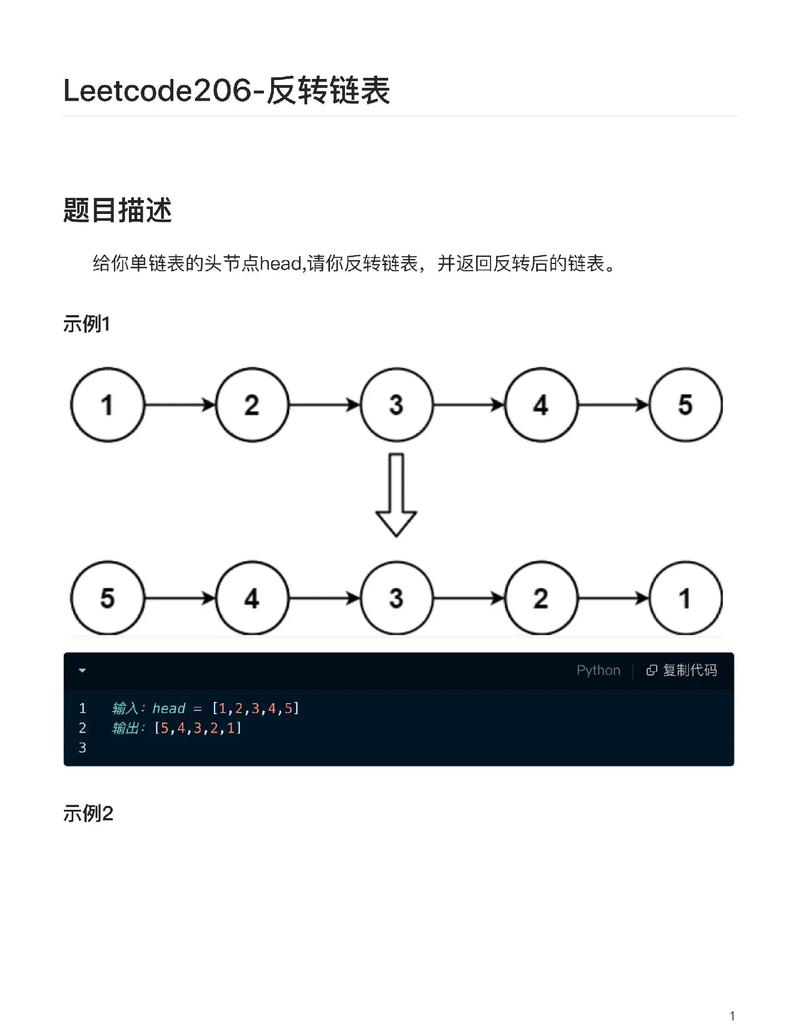
实现一个方法通过头结点来遍历链表打印出每个链表工具,如下所示。
// 打印链表的方法,便于测试public static void printLinkedList(ListNode head) { ListNode current = head; while (current != null) { System.out.print(current.val + " -> "); current = current.next; } System.out.println("null");}完全代码实现
// 定义链表节点类class ListNode { int val; ListNode next; ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; this.next = null; }}public class ArrayToLinkedList { // 将数组转换成链表的方法 public static ListNode arrayToLinkedList(int[] array) { if (array == null || array.length == 0) { return null; // 如果数组为空,返回null } // 创建链表头节点 ListNode head = new ListNode(array[0]); ListNode current = head; // 遍历数组,创建链表节点并链接 for (int i = 1; i < array.length; i++) { current.next = new ListNode(array[i]); current = current.next; } return head; // 返回链表头节点 } // 打印链表的方法,便于测试 public static void printLinkedList(ListNode head) { ListNode current = head; while (current != null) { System.out.print(current.val + " -> "); current = current.next; } System.out.println("null"); } public static void main(String[] args) { int[] array = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; ListNode head = arrayToLinkedList(array); printLinkedList(head); }}
上面的代码展示了如何将一个数组转换成一个单向链表操作,我们可以根据这个代码对干系实现进行扩展,例如我们可以添加其他类型数据的处理,或者是可以实现双向链表等操作。