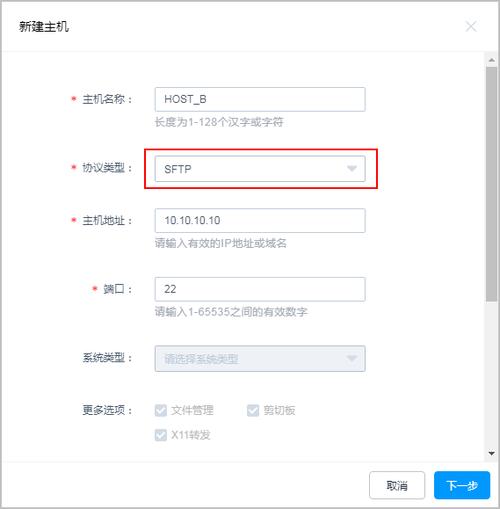
学过Java的同学都知道,我们新建文件,然后就可以写入数据了,但是Android却不一样,由于Android是 基于Linux的,我们在读写文件的时候,还需加上文件的操作模式,Android中的操作模式如下:
2.文件的干系操作方法

3.文件读写的实现
Android中的文件读写和Java中的文件I/O相同,流程也很大略,下面我们来写个大略的示例:
实现效果图:
PS:这里用的是仿照器,由于笔者的N5并没有root,看不到文件的存储目录,下面我们打开DDMS 的File Exploer可以看到,在data/data/<包名>/file中有我们写入的文件:
我们可以点击右上角的相应图标将文件导入到电脑中,并且打开验证写入的内容:
代码实现:
首先是布局文件:main_activity.xml
<LinearLayout xmlns:android=\公众http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android\公众
xmlns:tools=\公众http://schemas.android.com/tools\公众
android:id=\公众@+id/LinearLayout1\公众
android:layout_width=\公众match_parent\公众
android:layout_height=\公众match_parent\"大众
android:orientation=\"大众vertical\"大众
tools:context=\"大众com.jay.example.filedemo1.MainActivity\"大众>
<TextView
android:layout_width=\公众wrap_content\"大众
android:layout_height=\"大众wrap_content\"大众
android:text=\公众@string/nametitle\"大众 />
<EditText
android:id=\公众@+id/editname\"大众
android:layout_width=\公众match_parent\"大众
android:layout_height=\公众wrap_content\公众 />
<TextView
android:layout_width=\"大众wrap_content\公众
android:layout_height=\公众wrap_content\"大众
android:text=\公众@string/detailtitle\"大众 />
<EditText
android:id=\公众@+id/editdetail\公众
android:layout_width=\"大众match_parent\公众
android:layout_height=\公众wrap_content\"大众
android:minLines=\"大众2\"大众 />
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width=\"大众fill_parent\"大众
android:layout_height=\"大众wrap_content\公众
android:orientation=\"大众horizontal\"大众>
<Button
android:id=\"大众@+id/btnsave\"大众
android:layout_width=\"大众wrap_content\"大众
android:layout_height=\"大众wrap_content\公众
android:text=\"大众@string/btnwrite\公众 />
<Button
android:id=\"大众@+id/btnclean\公众
android:layout_width=\"大众wrap_content\"大众
android:layout_height=\"大众wrap_content\公众
android:text=\"大众@string/btnclean\"大众 />
</LinearLayout>
<Button
android:id=\"大众@+id/btnread\公众
android:layout_width=\"大众wrap_content\公众
android:layout_height=\"大众wrap_content\"大众
android:text=\公众@string/btnread\"大众 />
</LinearLayout>
然后我们来写一个文件帮忙类:FileHelper.java
/
Created by Jay on 2015/9/1 0001.
/
public class FileHelper {
private Context mContext;
public FileHelper() {
}
public FileHelper(Context mContext) {
super();
this.mContext = mContext;
}
/
这里定义的是一个文件保存的方法,写入到文件中,所以是输出流
/
public void save(String filename, String filecontent) throws Exception {
//这里我们利用私有模式,创建出来的文件只能被本运用访问,还会覆盖原文件哦
FileOutputStream output = mContext.openFileOutput(filename, Context.MODE_PRIVATE);
output.write(filecontent.getBytes()); //将String字符串以字节流的形式写入到输出流中
output.close(); //关闭输出流
}
/
这里定义的是文件读取的方法
/
public String read(String filename) throws IOException {
//打开文件输入流
FileInputStream input = mContext.openFileInput(filename);
byte[] temp = new byte[1024];
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(\"大众\公众);
int len = 0;
//读取文件内容:
while ((len = input.read(temp)) > 0) {
sb.append(new String(temp, 0, len));
}
//关闭输入流
input.close();
return sb.toString();
}
}
末了是MainActivity.java,我们在这里完成干系操作:
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnClickListener {
private EditText editname;
private EditText editdetail;
private Button btnsave;
private Button btnclean;
private Button btnread;
private Context mContext;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
mContext = getApplicationContext();
bindViews();
}
private void bindViews() {
editdetail = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.editdetail);
editname = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.editname);
btnclean = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnclean);
btnsave = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnsave);
btnread = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnread);
btnclean.setOnClickListener(this);
btnsave.setOnClickListener(this);
btnread.setOnClickListener(this);
}
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
switch (v.getId()) {
case R.id.btnclean:
editdetail.setText(\公众\"大众);
editname.setText(\"大众\"大众);
break;
case R.id.btnsave:
FileHelper fHelper = new FileHelper(mContext);
String filename = editname.getText().toString();
String filedetail = editdetail.getText().toString();
try {
fHelper.save(filename, filedetail);
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), \公众数据写入成功\"大众, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), \"大众数据写入失落败\"大众, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
break;
case R.id.btnread:
String detail = \"大众\"大众;
FileHelper fHelper2 = new FileHelper(getApplicationContext());
try {
String fname = editname.getText().toString();
detail = fHelper2.read(fname);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), detail, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
break;
}
}
}
4.读取SD卡上的文件
读取流程图:
代码示例:
运行效果图:
同样打开DDMS的File Explorer,在旧版本的系统上我们可以直接在mmt\sdcard上找到,但是新版本 的就可能须要我们自己找找了,首先我们来到这个路径下:
点开sdcard,但是没东西,我们连续找唠叨后面这个/storage/emulated/legacy下找:
好吧,他又跳到别的地方去了,我们连续找/storage/shell/emilated/0
果真找到了,我们在SD卡里天生的test.txt!
导出到电脑看下里面的内容:
嘿嘿,果真读写SD卡成功~接下来我们来看下代码是怎么写的:
代码实现:
main_activity.xml:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android=\"大众http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android\"大众
xmlns:tools=\"大众http://schemas.android.com/tools\"大众
android:id=\"大众@+id/LinearLayout1\"大众
android:layout_width=\公众match_parent\公众
android:layout_height=\"大众match_parent\"大众
android:orientation=\"大众vertical\"大众
tools:context=\公众com.jay.example.filedemo2.MainActivity\公众>
<TextView
android:layout_width=\公众wrap_content\"大众
android:layout_height=\"大众wrap_content\"大众
android:text=\"大众清输入文件名\"大众 />
<EditText
android:id=\公众@+id/edittitle\公众
android:layout_width=\公众match_parent\"大众
android:layout_height=\"大众wrap_content\"大众
android:hint=\"大众文件名\公众 />
<TextView
android:layout_width=\"大众wrap_content\公众
android:layout_height=\"大众wrap_content\"大众
android:text=\"大众清输入文件内容\"大众 />
<EditText
android:id=\"大众@+id/editdetail\"大众
android:layout_width=\公众match_parent\"大众
android:layout_height=\"大众wrap_content\"大众
android:hint=\"大众文件内容\公众 />
<Button
android:id=\"大众@+id/btnsave\公众
android:layout_width=\"大众wrap_content\"大众
android:layout_height=\公众wrap_content\公众
android:text=\"大众保存到SD卡\"大众 />
<Button
android:id=\"大众@+id/btnclean\公众
android:layout_width=\"大众wrap_content\公众
android:layout_height=\公众wrap_content\"大众
android:text=\"大众清空\公众 />
<Button
android:id=\公众@+id/btnread\公众
android:layout_width=\"大众wrap_content\公众
android:layout_height=\"大众wrap_content\"大众
android:text=\"大众读取sd卡中的文件\公众 />
</LinearLayout>
接着我们来写一个SD操作类: SDFileHelper.java
/
Created by Jay on 2015/9/1 0001.
/
public class SDFileHelper {
private Context context;
public SDFileHelper() {
}
public SDFileHelper(Context context) {
super();
this.context = context;
}
//往SD卡写入文件的方法
public void savaFileToSD(String filename, String filecontent) throws Exception {
//如果手机已插入sd卡,且app具有读写sd卡的权限
if (Environment.getExternalStorageState().equals(Environment.MEDIA_MOUNTED)) {
filename = Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory().getCanonicalPath() + \"大众/\公众 + filename;
//这里就不要用openFileOutput了,那个是往手机内存中写数据的
FileOutputStream output = new FileOutputStream(filename);
output.write(filecontent.getBytes());
//将String字符串以字节流的形式写入到输出流中
output.close();
//关闭输出流
} else Toast.makeText(context, \"大众SD卡不存在或者不可读写\"大众, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
//读取SD卡中文件的方法
//定义读取文件的方法:
public String readFromSD(String filename) throws IOException {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(\"大众\公众);
if (Environment.getExternalStorageState().equals(Environment.MEDIA_MOUNTED)) {
filename = Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory().getCanonicalPath() + \"大众/\公众 + filename;
//打开文件输入流
FileInputStream input = new FileInputStream(filename);
byte[] temp = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
//读取文件内容:
while ((len = input.read(temp)) > 0) {
sb.append(new String(temp, 0, len));
}
//关闭输入流
input.close();
}
return sb.toString();
}
}
接着MainActivity.java实现干系逻辑:
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnClickListener{
private EditText editname;
private EditText editdetail;
private Button btnsave;
private Button btnclean;
private Button btnread;
private Context mContext;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
mContext = getApplicationContext();
bindViews();
}
private void bindViews() {
editname = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.edittitle);
editdetail = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.editdetail);
btnsave = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnsave);
btnclean = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnclean);
btnread = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnread);
btnsave.setOnClickListener(this);
btnclean.setOnClickListener(this);
btnread.setOnClickListener(this);
}
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
switch (v.getId()){
case R.id.btnclean:
editdetail.setText(\"大众\"大众);
editname.setText(\"大众\公众);
break;
case R.id.btnsave:
String filename = editname.getText().toString();
String filedetail = editdetail.getText().toString();
SDFileHelper sdHelper = new SDFileHelper(mContext);
try
{
sdHelper.savaFileToSD(filename, filedetail);
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), \"大众数据写入成功\"大众, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), \公众数据写入失落败\"大众, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
break;
case R.id.btnread:
String detail = \公众\"大众;
SDFileHelper sdHelper2 = new SDFileHelper(mContext);
try
{
String filename2 = editname.getText().toString();
detail = sdHelper2.readFromSD(filename2);
}
catch(IOException e){e.printStackTrace();}
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), detail, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
break;
}
}
}
末了别忘却在AndroidManifest.xml写上读写SD卡的权限哦!
<!-- 在SDCard中创建与删除文件权限 -->
<uses-permission android:name=\"大众android.permission.MOUNT_UNMOUNT_FILESYSTEMS\"大众/>
<!-- 往SDCard写入数据权限 -->
<uses-permission android:name=\"大众android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE\"大众/>
5.关于原生仿照器SD卡的问题
如果是真机调试的话常日都是可以的,对付原生虚拟机的话就问题多多了,再我们前面利用 Environment.getExternalStorageState().equals(Environment.MEDIA_MOUNTED)可能 一贯返回的是false,便是SD卡不存在,这个是紧张的问题,现在新版本的SDK都会在 创建AVD的时候会同时申请一块SD卡的存储区域的
对付旧版本的sdk或者其他缘故原由可能须要手动关联下sd卡,设置如下:
①找到创建好的avd的镜像的路径:
点击打开avd界面,点击detail,查看avd镜像的目录下
②来到avd镜像所在的路径下,复制sdcard.img的路径:
比如我的:-sdcard C:\Users\Administrator.android\avd\Jay4.2.avd\sdcard.img
③接着点击
来到以下界面:
末了apply以下,然后Run就可以了!
6.读取raw和assets文件夹下的文件
相信大家对两个文件夹并不陌生,如果我们不想自己的文件被编译成二进制文件的话, 我们可以把文件放到这两个目录下,而两者的差异如下:
res/raw:文件会被映射到R.java文件中,访问的时候直接通过资源ID即可访问,而且 他不能有目录构造,便是不能再创建文件夹assets:不会映射到R.java文件中,通过AssetManager来访问,能有目录构造,即, 可以自行创建文件夹读取文件资源:
res/raw:
InputStream is =getResources().openRawResource(R.raw.filename);
assets:
AssetManager am = getAssets();
InputStream is = am.open(\"大众filename\"大众);
代码下载:
FileDemo.zip:下载 FileDemo.zipFileDemo2.zip:下载 FileDemo2.zip本节小结:
好的,关于Android的数据存储与访问的第一节——文件读写就到这里,如果在学习本文中 碰着什么问题,或者以为有些疏忽的地方,欢迎提出,万分感激,感激~